
Anyone who runs an online shop with a large product range usually also uses a large number of text and image files in the shop system. For example, various product descriptions and photos are included in order to provide potential buyers with as much information about the product as possible.
The disadvantage of this is that retrieving image files often requires a lot of bandwidth. Under certain circumstances, this can have a negative impact on the performance of the shop. Therefore, in this article we will look at content delivery networks and the advantages and disadvantages of their use in e-commerce.
What is a CDN?
A Content Delivery Network (in the following we will use the abbreviated form "CDN") is a network of interconnected servers that are distributed across different regional locations, so-called "PoPs (Points of Presence)".
Such a network is suitable, for example, to quickly deliver media content such as large image or video files to the end user's browser - no matter from which part of the world it is accessed. Even during peak loads, a CDN ensures that the content remains accessible and is played out with high performance due to scaling storage capacities and lower bandwidth utilisation.
Often unnoticed by the end user, CDNs have long been part of our everyday lives. For example, streaming services, social media platforms, software providers or website operators use a CDN to play out content without delay via servers located in the physical vicinity of the end user.
How does a CDN work?
Those who use a CDN first store the content of their web application on an origin server. This content is then distributed to a large number of geographically distributed replica servers. As their name suggests, these replica servers thus contain copies of the content that is on the origin server. Depending on the region from which a client sends a request, a suitable replica server is selected via a request routing system. The contents are then retrieved via this server and played out to the client.
The so-called accounting system decides which replica server is selected. In addition to the load of the replica server and the geographical proximity, this also checks factors such as the quality of the network connection between server and client. Depending on the CDN provider, however, the exact checking process can vary.
Once a suitable replica server has been selected with the help of the request routing system, the request is redirected to it. DNS-based request routing is the most frequently used method of forwarding. The request is answered to a DNS server, which is usually provided by the end user's Internet provider. In this way, the approximate geo-position of the end user can be determined.
Alternatively, the forwarding can also take place on the server side with the help of an HTTP status code 302. In diesem Fall gibt der Ursprungsserver nach Eingang eines Requests den HTTP-Statuscode an den Client zurück und teilt diesem so einen Replica-Server zu. Der Client führt nun automatisch einen weiteren Request an den zugewiesenen Replica-Server durch.
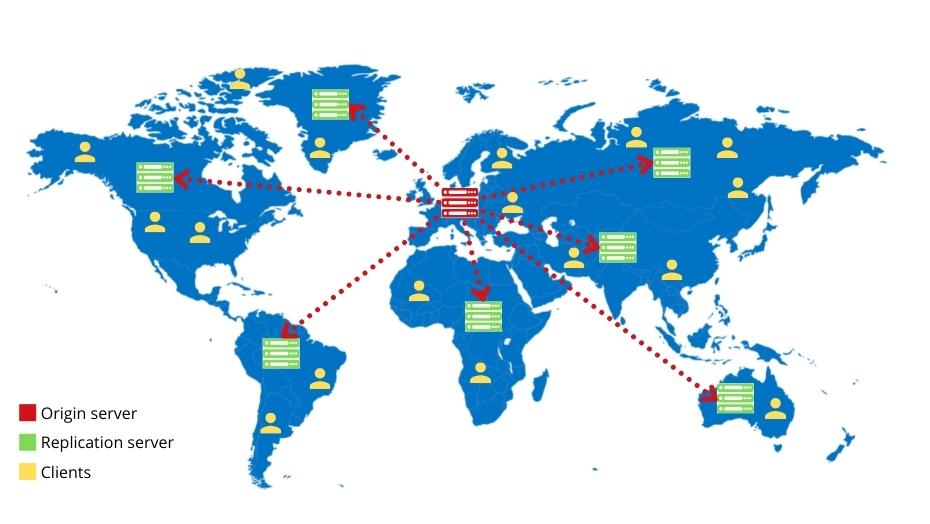 Exemplary structure of a content delivery network I Grafik: maxcluster
Exemplary structure of a content delivery network I Grafik: maxcluster
Advantages of CDNs
Those who choose to use a CDN can often benefit from some of the following.
Fast delivery of data
With incoming requests, static resources such as images, videos, documents or HTML pages are delivered directly from the assigned replica server to the client. As the shop operator, you decide which elements of your shop you want to outsource from the web server to the CDN. Especially the delivery of large media files via the CDN reduces the load on the web server and leads to faster loading times for the end user.
The geographical distance between server and client as well as the quality of the network connection are also relevant for the loading time. If, for example, a user from the USA accesses a website hosted on a server in Germany, he or she must accept longer loading times due to the distance.
If, on the other hand, parts of the website are outsourced to a CDN, the corresponding content is instead delivered by a replica server that is located close to the client. In this way, the loading time is sometimes considerably reduced.
Global availability and redundancy
Even with high traffic, an online shop using a CDN remains accessible to the end user. This is because the CDN is able to distribute large data traffic in such a way that no performance bottlenecks occur.
Due to the extensive geographical distribution, a CDN is also less susceptible to hardware failures. However, if the server fails, the shop will no longer function despite the CDN, at the latest when the checkout is executed.
Lower resource requirements
Using a CDN reduces the bandwidth of your servers. If you operate your own server infrastructure, it will be spared by reducing the load. This can have a positive effect on the service life. If, on the other hand, you work with a hosting provider, you reduce your need for resources by using a CDN. This results in lower hosting costs.
Higher protection against DDoS attacks
A CDN's request routing system can provide "natural" protection against cyber-attacks such as DDoS attacks or web-based exploits. However, this only applies to CDNs that are connected upstream of the web server. Since incoming requests are directly redirected here, the origin server is more difficult for attackers to reach. With classic CDNs, on the other hand, only the content is delivered, while the request is routed directly to the origin server.
Since the number of cyber attacks is increasing worldwide, many CDN providers also take extensive security measures to protect your data as best as possible. In most cases, however, these deeper protective functions are only offered at extra cost and must also be configured individually.
Disadvantages of CDNs
Although a CDN brings with it many advantages, its use can also create shortcomings. Whether one or more aspects of a CDN become a disadvantage usually depends on the individual requirements and metrics of your online shop.
CDN quality
When choosing a CDN, the speed should be checked. If a CDN has poor bandwidth, content will ultimately be delivered slower than if it came directly from the origin server. This is also true in cases where a client is geographically close to a replica server. Especially with a good hosting setup, a CDN can also have a negative impact on performance.
In addition, CDNs represent an additional "point of failure": If the CDN itself fails or has a malfunction, your web application is also no longer accessible.
Technical effort
Before you decide to use a CDN, you should check which requirements you have with regard to your online shop and whether the services of the CDN provider of your choice cover enough of them.
The commissioning of a CDN involves a great deal of technical effort and requires the corresponding know-how. Since the data is no longer located on a central server, the ongoing operation also causes more effort.
Less data control
If you decide to use a CDN, you also lose sole control over the data you provide in the context of your web application. On the one hand, this is due to the fact that a large number of the replica servers provided are located abroad and your data is transmitted there. On the other hand, the IP address of your shop visitors is transmitted to the respective replica server.
Both can lead to data protection problems. Therefore, check in advance whether the CDN provider of your choice contractually guarantees you DSGVO-compliant data processing.
Dynamic content
A CDN is designed to deliver static data and offers many advantages in terms of performance and availability of your web application. However, a CDN is not suitable for the delivery of dynamic content, such as shopping baskets, which are particularly important in e-commerce.
Since this content is partly user-dependent and constantly changing, it is not suitable for loading from the cache of a replica server. In such cases, incoming requests must be forwarded to the origin server.
High costs
Even though a lower resource requirement in terms of hosting may sound tempting at first, high costs are often associated with the use of CDN services. For smaller online shops with a lower budget, the use of a CDN can therefore be very expensive.
SEO
Although a fast loading time is generally advantageous in terms of search engine ranking, the use of a CDN also harbours potential pitfalls. If optimisations such as updating snippets are carried out, it must first be ensured that the changes have also been transferred from the original to the replica servers. Normally, this happens automatically, but delays can occur. The result is that content such as images is sometimes delivered to the end user with a delay after a change. This can have a negative effect on search engine rankings.
Risk of cyber attacks
Although the architecture of a CDN increases security with regard to DDoS attacks, it also offers a larger attack surface for criminal hackers due to the high number of servers. If you are considering using a CDN, you should therefore be very careful with the outsourcing of sensitive data.
Other methods of performance optimisation
To improve the performance or availability of an online shop, you do not necessarily have to resort to a CDN. Although they are not mutually exclusive in most cases, the following aspects represent possible alternatives to a CDN.
Application optimisation
If it is technically compatible, you should operate your shop system with one of the newer PHP versions. In most cases, new PHP releases are accompanied by significant performance improvements. With PHP 8.0, for example, you benefit from the JIT compiler introduced there. The latest version PHP 8.1 also has interesting new functions.
With efficient full-page caching, you can drastically reduce the loading time of your online shop. A suitable tool for this is the HTTP cache proxy Varnish. This is connected in front of a web server and delivers static content from the cache to the client. If you use several web servers, Varnish can also be used as a load balancer. In the linked blog post you can read interesting details about Varnish.
Medium and larger online shops can also benefit from moving the cache and sessions from the file system to Redis. We have summarised how online shops benefit most from Redis in a standalone blog series.
Web page compression
If you use a large number of text and binary files such as images or videos in your online shop, you can make them smaller in order to reduce the resource requirements during transmission. There are various methods for doing this.
While superfluous spaces or line breaks can simply be removed from text files, lossless compression of image files is somewhat more complex. One possibility, for example, is to convert files into more modern image formats.
You can also compress your online shop with the gzip or Brotli module to reduce the loading time. In the article linked here, we present various methods of website compression in detail.
Conclusion
Fast and location-independent delivery of data, global availability, lower hardware requirements: the use of a content delivery network often brings advantages for shop operators, but under certain circumstances it can also prove to be a disadvantage.
Whether the use of a CDN makes sense depends on the individual requirements of the online shop and the quality of the technical setup. In case of doubt, a comparison of the total loading time (including assets) with and without CDN can provide information about possible performance potential.
Larger online shops that are internationally positioned and have an extensive product range usually benefit the most from the use of a CDN. Smaller online shops with a regional focus and a less extensive range of products may gain greater added value if they focus on one or more of the alternatives. The optimisation of one's own web application in terms of performance is often much more cost-efficient and possible with less effort.
For maxcluster customers, it is usually not necessary to use a CDN for performance or availability reasons. Our Tier III+ data centre in Frankfurt am Main benefits from its proximity to DE-CIX, the world's largest Internet node. Therefore, shops hosted at maxcluster are easily accessible throughout Europe and availability in the USA is also usually guaranteed.
However, if end customers outside Europe are to be served or if another function of a CDN brings shop operators significant advantages, the use of a CDN may well be worthwhile.
Are you looking for a competent and reliable hosting partner or would you like to find out more about the Managed Hosting Services at maxcluster? Then feel free to contact our consulting team by phone at +49 5251 4141 350 or by e-mail at beratungmaxcluster.de.
